Is Sugar Addictive? Unpacking the Myths and Facts
Is sugar addictive? This question sparks intense debate among nutrition experts and health enthusiasts alike. While sugar does not meet the strict clinical criteria required for classification as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, its ability to provoke cravings and compulsive consumption behaviors raises concerns. Many people find themselves reaching for ultra-processed foods packed with added sugar, leading to a cycle of sugar addiction that can undermine healthy eating habits. Understanding the effects of added sugar on our lifestyles is essential, as these cravings can lead to health complications, prompting us to explore our relationships with sugar more deeply.
The concept of sugar dependence encompasses more than just physical cravings; it also delves into the psychological attachments formed with sugary treats. Many individuals experience powerful urges for sweets, often finding it challenging to resist indulgence in processed foods high in added sugars. As we explore the dynamics of sugar addiction, it’s crucial to acknowledge the hidden effects of these sugary substances on our well-being and daily lives. Considering this, we might also reframe sugar cravings as a behavioral response to the widespread availability of enticing, sugary options in our diets. By recognizing the subtle interplay of sugar and our eating habits, we can pave the way toward creating healthier eating patterns.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
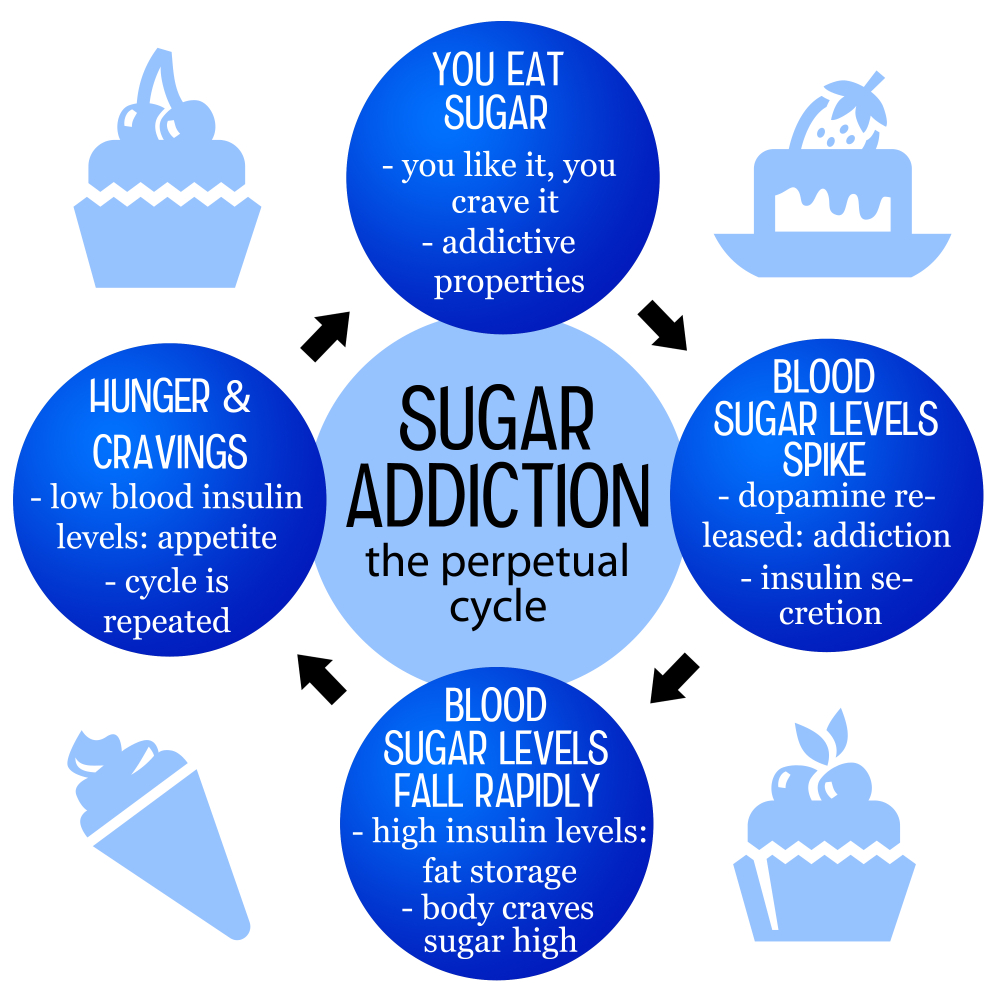
Sugar addiction is a complex phenomenon that engages physical dependence and psychological cravings. Studies suggest that sugar can trigger the same reward centers in the brain as illicit drugs, leading to compulsive eating behaviors and persistent cravings for sugary foods. Unlike substances such as alcohol or nicotine, sugar does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction; however, many individuals report experiencing withdrawal symptoms like headaches and mood swings when they drastically cut sugar from their diets.
This apparent dichotomy prompts a critical examination of sugar in our lives. The presence of added sugars in ultra-processed foods creates a culture of excess, where individuals may find themselves reaching for sugary snacks and beverages more frequently. Understanding the impact of sugar on our mental state is crucial for developing healthy eating habits. It highlights the necessity for a balanced approach where sugar is consumed in moderation, ensuring it enhances rather than detracts from our overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like nicotine or alcohol?
While sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive in the same clinical sense as nicotine or alcohol. Sugar interacts with brain pathways and can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when eliminated abruptly, but moderation is key.
What are the effects of added sugar on cravings?
Added sugar in processed foods can amplify cravings due to its palatability. When people consume highly processed foods, they’re likely to experience increased desire for more sugar, which can lead to habitual consumption and potential issues with sugar addiction.
How can I maintain healthy eating habits regarding sugar consumption?
To promote healthy eating habits, it is essential to monitor added sugar intake. Reading food labels and gradually reducing sugar consumption can help manage cravings without going cold turkey, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Are there withdrawal symptoms from sugar cravings?
Yes, when individuals reduce or eliminate sugar from their diets, they may experience withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, and, in some cases, dizziness. This can mimic the withdrawal effects seen with more addictive substances.
What is the recommended amount of added sugar for a healthy diet?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children to avoid the potential negative health effects associated with high sugar consumption.
How do processed foods relate to sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them particularly addictive. Their accessibility and palatability can enhance cravings, leading to increased consumption and potential sugar addiction.
Is some sugar necessary in our diets?
Yes, sugar naturally occurs in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. While it’s important to limit added sugars, a moderate amount of naturally occurring sugar can enhance flavor and is necessary for a balanced diet.
What strategies can help manage sugar cravings effectively?
To effectively manage sugar cravings, consider gradually reducing added sugar intake, choosing whole foods over processed options, and staying hydrated. This approach can lessen cravings without causing harsh withdrawal symptoms.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | The classification of sugar as addictive is heavily debated, and it’s not officially classified as such under clinical criteria, unlike substances like alcohol and nicotine. |
| Cravings and Withdrawal Symptoms | Sugar can cause cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms, but they are less severe compared to those resulting from addictive drugs. |
| Need for Sugar | Sugar is essential in various foods like fruits and dairy, and some sugar is necessary for a balanced diet. |
| Consumption Recommendations | The average American consumes around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily; the recommended limit is 6-9 teaspoons depending on gender. |
| Gradual Reduction | Removing sugar abruptly can have negative effects, so it’s better to decrease sugar intake gradually. |
| Conclusion | While sugar has some addictive qualities, categorizing it alongside drugs can be counterproductive, as it plays a vital role in our diets and should be consumed in moderation. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This crucial question has generated a significant amount of discourse among nutrition experts. Though it does not fall under the same category as substances like alcohol and nicotine, sugar can trigger cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms due to its presence in ultra-processed foods. Moderation is key; while we need some sugar in our diets for flavor and energy, the excessive consumption of added sugars can lead to health issues. Therefore, it is essential to approach sugar with an understanding of its role in our nutrition and to consume it mindfully.
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |