Age-Related Brain Diseases: 17 Identified Risk Factors
Age-related brain diseases, including conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, pose significant health challenges as we grow older. Recent research has unveiled 17 modifiable risk factors that can help mitigate these risks, emphasizing the potential for behavioral interventions to enhance brain health. Factors such as high blood pressure, kidney disease, and lifestyle choices like diet and physical activity have been shown to influence the likelihood of developing these debilitating conditions. To reduce the impact of age-related brain diseases, adopting proactive brain health tips and understanding risk factors for dementia become crucial. By addressing these interconnected issues, we can improve quality of life and ensure healthier aging for individuals everywhere.
The topic of age-related cognitive decline encompasses a variety of conditions including cerebrovascular accidents, neurodegenerative disorders, and mood disturbances prevalent in older adults. Recent findings have identified crucial lifestyle and health-related factors that significantly influence the likelihood of experiencing these age-related cognitive impairments. Understanding how elements such as dietary habits, physical activity levels, and social engagement can affect brain vitality is essential for fostering better health outcomes. Furthermore, exploring strategies for stroke prevention and addressing mental health challenges in later life can further assist in minimizing the incidence of these conditions. By emphasizing brain wellness, we can equip individuals with the necessary tools to enhance their cognitive resilience and overall quality of life.
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases
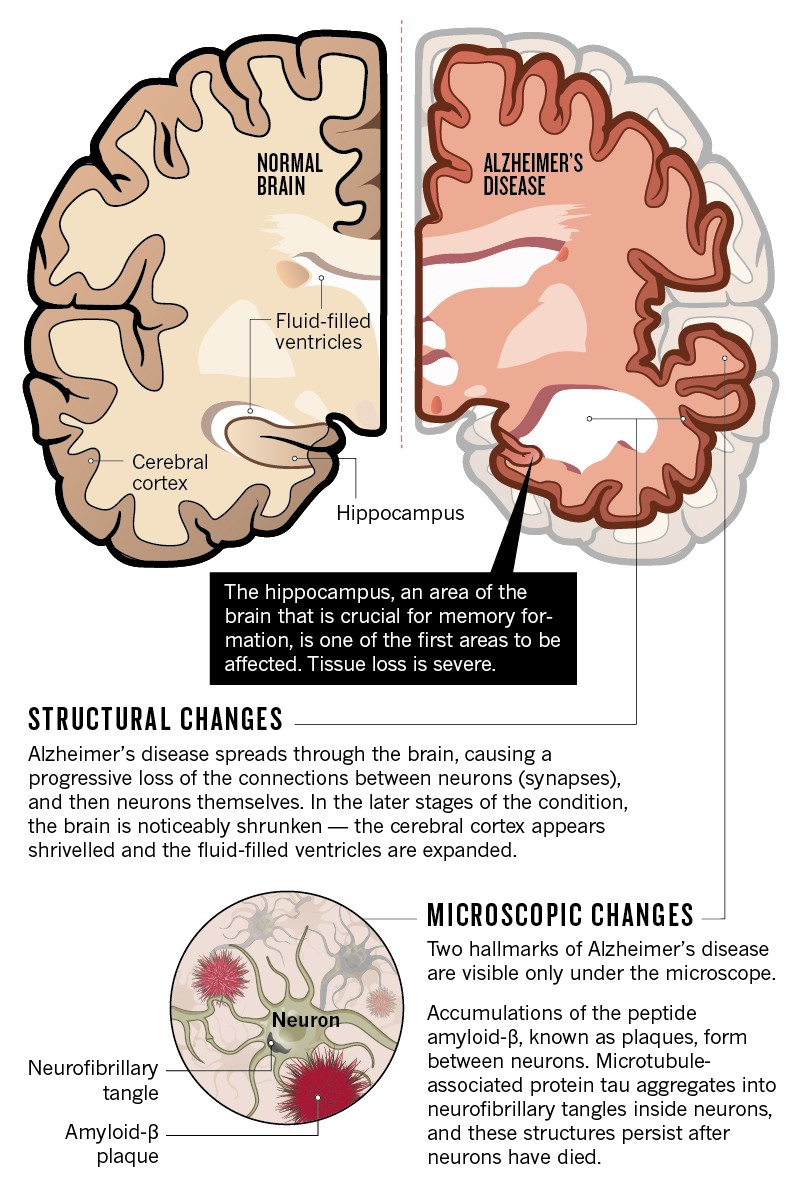
Age-related brain diseases, including dementia, stroke, and late-life depression, are complex conditions that significantly impact the older population. These diseases often intersect, sharing common risk factors that can elevate an individual’s chances of developing multiple conditions over time. For this reason, healthcare researchers are focusing on understanding these interconnected factors, which is crucial for effective prevention and intervention strategies. Identifying modifiable risk factors allows individuals to make lifestyle changes that can potentially mitigate their risk, fostering better brain health as they age.
Recent research from Mass General Brigham has highlighted 17 risk factors that are significantly associated with age-related brain diseases. These factors include blood pressure, kidney disease, diet, and physical activity, among others. Understanding how these elements influence brain health is essential for developing comprehensive approaches to address and reduce the burden of these conditions. In addition, this awareness encourages individuals to take proactive measures that can help maintain cognitive function and overall mental wellness.
Strategies to Lower the Risk of Dementia
Modifying lifestyle choices is one of the most effective strategies for lowering the risk of dementia. The study indicates that factors such as maintaining healthy blood pressure, managing diabetes, and engaging in regular physical activity play a pivotal role in keeping the brain healthy. Incorporating brain-healthy diets rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids can also support cognitive function. Individuals can reduce their likelihood of developing dementia by actively engaging in these lifestyle modifications and making informed choices based on their health status.
Moreover, engaging in social activities and maintaining a sense of purpose can significantly impact mental health and cognitive longevity. Research suggests that social engagement not only combats loneliness but also strengthens neural connections that can degrade over time. Therefore, individuals looking to reduce their risk of dementia should consider incorporating social hobbies into their routines, such as participating in community events or joining clubs that align with their interests.
The Impact of Modifiable Risk Factors
Modifiable risk factors are crucial areas where individuals can exert control over their health outcomes. The 17 identified factors from the recent study provide a roadmap for people seeking to prevent age-related brain diseases. Blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and lifestyle habits such as smoking and alcohol consumption are key areas that individuals can manage to see a positive impact on their brain health. By making changes in these areas, people can significantly decrease their chances of encountering conditions like stroke and late-life depression.
The critical takeaway from this research is that many of these risk factors are intertwined, meaning improvements in one area can lead to benefits in others. For instance, adopting a healthier diet can lead to better blood pressure control and weight management, thereby simultaneously reducing the risk of dementia and depression. By focusing on holistic approaches that address multiple risk factors concurrently, individuals can enhance their overall cognitive health throughout their lives.
Brain Health Tips for Seniors
Maintaining brain health involves a multifaceted approach that combines physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being. Simple habits, such as regular physical exercise and balanced nutrition, can significantly affect brain function. Engaging in cognitive activities, such as puzzles or learning new skills, can also keep the brain active and productive. Sanity checks like ensuring adequate sleep and managing stress levels through mindfulness techniques or social activities contribute to long-term cognitive wellness.
Additionally, seniors are encouraged to prioritize their social connections. Regularly scheduled interactions with family and friends can provide emotional support and cognitive stimulation, reducing feelings of isolation that can contribute to depression and cognitive decline. By adhering to these brain health tips, seniors have the potential to enhance their quality of life, promoting both mental and physical wellness as they age.
Late-Life Depression Solutions
Addressing late-life depression is pivotal due to its dual impact on mental health and the potential risk of developing age-related brain diseases. Various solutions exist, including psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has shown effectiveness in promoting positive coping strategies and reducing symptoms of depression among older adults. Combining therapy with regular physical activity and social engagement increases overall efficacy in treatment.
Moreover, creating structured daily routines that incorporate enjoyable activities can provide motivation and purpose in life, which are critical for preventing feelings of depression. Seniors can benefit significantly from engaging in community programs that provide social support, such as exercise classes or group workshops that emphasize learning and interaction. By tackling late-life depression head-on, individuals can reduce their risk of comorbid conditions like dementia and stroke.
Stroke Prevention Techniques
Preventing strokes is vital for safeguarding brain health, particularly in older adults. Effective stroke prevention strategies hinge on managing modifiable risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and unhealthy cholesterol levels. Routine health screenings and consultations can aid in monitoring these markers, facilitating early intervention when necessary. Simple lifestyle tweaks, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet and maintaining an active lifestyle, have proven essential in minimizing stroke risk.
Additionally, education plays a crucial role in stroke prevention. Knowing the warning signs of a stroke allows for timely medical intervention, significantly mitigating potential damage. Public health campaigns that raise awareness of the symptoms, alongside community resources for health assessments, empower individuals to take proactive steps towards protecting their brain health. By prioritizing stroke prevention methods, older adults can significantly decrease their overall risk of age-related brain diseases.
Exploring the Role of Diet in Brain Health
Diet is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone of brain health, particularly in preventing age-related disorders. Research underscores the importance of balanced nutrition, noting that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can enhance cognitive function. Specific dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, have been linked to lower incidences of dementia and depression among seniors, highlighting the power of nutrition in influencing brain longevity.
Furthermore, specific nutrients play critical roles in cognitive health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, for instance, contribute to the maintenance of neural function, while antioxidants help in combating oxidative stress within the brain. Hence, individuals should focus on integrating brain-boosting foods into their diets, recognizing that proper nutrition can be a significant modifiable risk factor for preventing diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression.
Physical Activity and Cognitive Function
The link between physical activity and cognitive function is well-established, with numerous studies demonstrating that regular exercise can protect against age-related cognitive decline. Engaging in physical activity promotes better blood circulation and enhances overall brain health, reducing the likelihood of diseases like dementia and stroke. The guidelines recommend that older adults aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week.
Incorporating exercises that challenge coordination and balance, such as tai chi or yoga, can further enhance cognitive vitality. Additionally, activities that combine physical exertion with social interaction, such as group fitness classes, foster not only physical health but also emotional well-being. Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines physical activity with social engagement is vital for maximizing cognitive resilience in aging individuals.
The Importance of Regular Health Screenings
Routine health screenings are instrumental in detecting potential risk factors for age-related brain diseases before they escalate. Regular visits to healthcare professionals can help monitor key indicators relevant to brain health, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood glucose. Early detection and management of these conditions empower individuals to take charge of their health, reducing the risk of developing serious complications like stroke and dementia.
Furthermore, health screenings facilitate productive conversations about lifestyle changes and preventive strategies tailored to individual needs. Individuals are encouraged to actively participate in their healthcare journey, scheduling regular check-ups and following through with recommendations from healthcare providers. By prioritizing routine screenings, older adults can not only safeguard their physical health but also maintain cognitive functioning as they age.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main risk factors for dementia, stroke, and late-life depression?
The main risk factors for age-related brain diseases like dementia, stroke, and late-life depression include diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney disease, fasting plasma glucose, high total cholesterol, alcohol consumption, poor diet, hearing loss, chronic pain, lack of physical activity, absence of purpose in life, poor sleep quality, smoking, low social engagement, chronic stress, untreated depression, and obesity. Modifying these factors can significantly lower the risk of developing these conditions.
Are there modifiable risk factors to prevent age-related brain diseases?
Yes, there are several modifiable risk factors that can help prevent age-related brain diseases, including maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels, managing diabetes, reducing alcohol intake, improving diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting adequate sleep, quitting smoking, and enhancing social engagement. By addressing these risk factors, individuals can reduce their risk of developing dementia, stroke, and late-life depression.
How can diet influence the risk of developing age-related brain diseases?
Diet plays a crucial role in brain health and can influence the risk of age-related brain diseases. A nutritious diet that is low in saturated fats and sugars while high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids may help mitigate the risk of dementia, stroke, and late-life depression. A poor diet, conversely, has been identified as a modifiable risk factor for these conditions.
What brain health tips can help prevent dementia and stroke?
To help prevent dementia and stroke, practice the following brain health tips: maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical exercise, manage stress effectively, ensure sufficient sleep, avoid smoking, limit alcohol intake, and foster social connections. Additionally, finding a sense of purpose in life can significantly benefit mental health, thus reducing the risks associated with age-related brain diseases.
How significant is the link between depression and age-related brain diseases?
Depression is significantly linked to age-related brain diseases such as dementia and stroke. Untreated depression is a major risk factor for these conditions, creating a cycle where individuals with depression may face a higher likelihood of developing dementia or experiencing stroke. Addressing depression through appropriate interventions can, therefore, be critical in reducing the risk of these connected brain diseases.
What role does physical activity play in brain health?
Physical activity is a vital modifiable risk factor for age-related brain diseases. Regular exercise helps improve blood flow, reduce stress, and enhance overall mood, thereby lowering the risk of dementia, stroke, and late-life depression. Engaging in both aerobic exercise and leisure activities that challenge the brain contributes positively to brain health.
Can social engagement reduce the risk of dementia and depression?
Yes, social engagement can significantly reduce the risk of dementia and depression. Strong social connections can provide emotional support, reduce stress, and foster a sense of belonging, which are all beneficial for mental health. Engaging in social activities is a crucial modifiable risk factor for preventing age-related brain diseases.
What is the Brain Care Score and how does it relate to age-related brain diseases?
The Brain Care Score is a tool developed by researchers to measure efforts in protecting brain health. It provides guidance on improving habits that can mitigate the risk of age-related brain diseases like dementia, stroke, and late-life depression. By assessing and addressing multiple modifiable risk factors, individuals can enhance their brain health and lower their risk of these interconnected conditions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Identification of Risk Factors | 17 modifiable factors that reduce the risk of age-related brain diseases. |
| Associated Diseases | The factors can lower the risk of stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. |
| Research Foundation | Conducted by researchers at Harvard-affiliated Mass General Brigham. |
| Publication | Findings published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. |
| Key High-Risk Factors | High blood pressure and severe kidney disease have the most significant impact. |
| Additional Factors | Includes diabetes, physical activity, diet, smoking, and social engagement. |
| Preventive Insights | Modifying any single factor can significantly lessen the risk. |
Summary
Age-related brain diseases, including dementia, stroke, and late-life depression, represent a growing health concern, especially as the population ages. This recent research highlights the potential for targeted interventions through the modification of 17 identified risk factors, many of which are modifiable with lifestyle changes. Understanding and addressing these risk factors can pave the way for innovative prevention strategies that could reduce the burden of these interconnected diseases, emphasizing the importance of proactive health management.
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |