Bile Imbalance Linked to Liver Cancer: Key Insights Revealed
Bile imbalance liver cancer emerges as a critical concern in the field of liver disease research, particularly due to its connection with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent studies have highlighted how irregularities in bile acid production, vital for digestion, can lead to severe liver ailments. This imbalance not only affects fat digestion but also disrupts essential metabolic processes, consequently increasing cancer risk. Insights into the YAP FXR signaling pathway reveal a promising avenue for liver cancer treatment, indicating that regulatory dysfunction can exacerbate liver damage and promote tumor development. By addressing these bile acids health issues, researchers aim to uncover effective therapeutic strategies to mitigate the progression of liver cancer.
The connection between bile fluctuations and liver malignancies, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a growing area of concern in understanding liver health. Bile acids, crucial for digesting dietary fats, play a significant role beyond their digestive functions—they also influence various metabolic pathways within the body. Disruption of bile acid equilibrium may lead to liver inflammation and contribute to the development of malignant tumors. Recent research into the molecular mechanisms, including YAP regulation and its impact on bile metabolism, sheds light on potential new treatments for liver cancer. As scientists continue to explore the complexities of liver disease, the significance of maintaining healthy bile acid levels becomes increasingly clear.
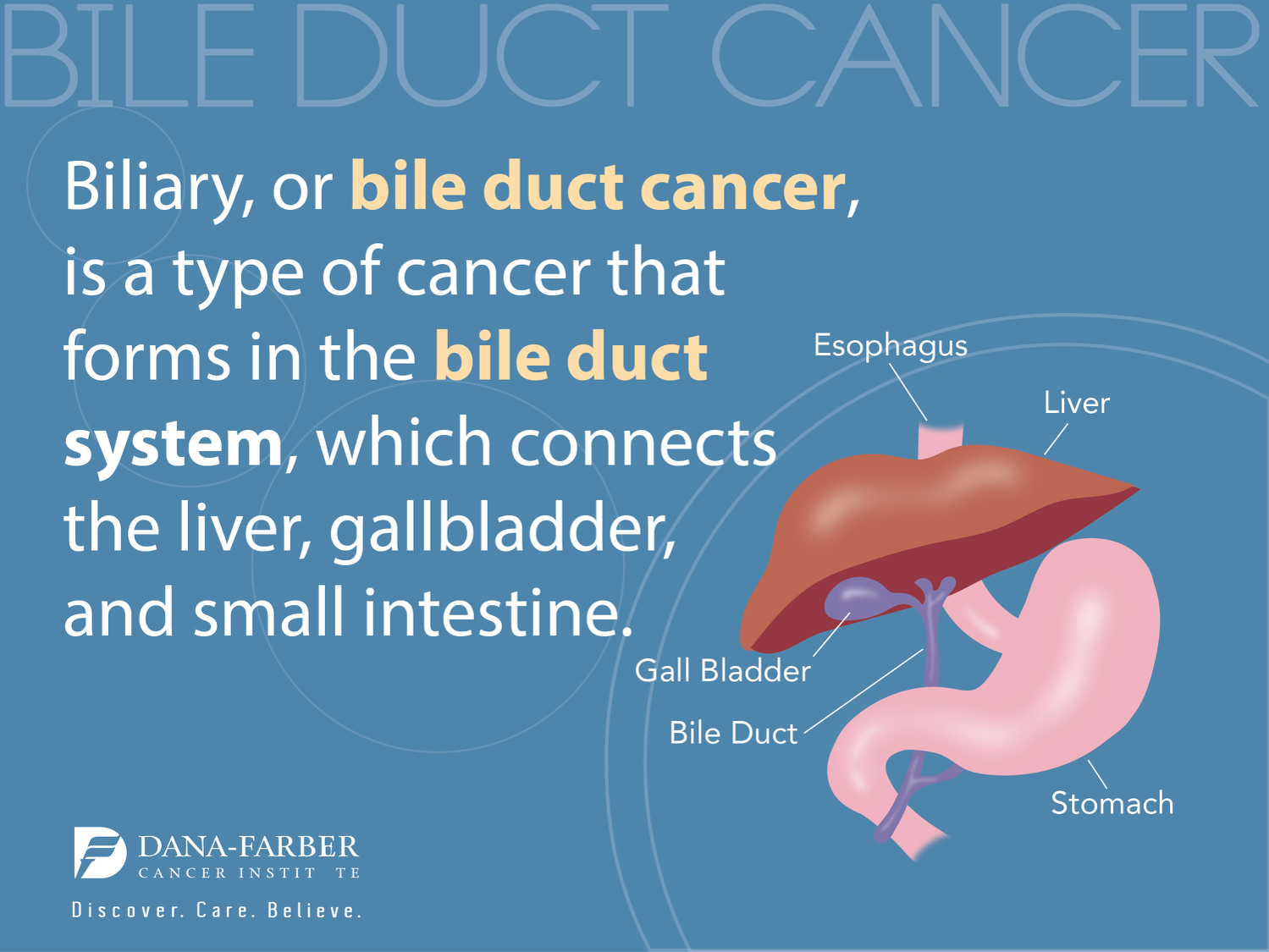
Understanding Bile Acids and Their Role in Liver Health
Bile acids are essential for the digestive process, facilitating the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins in the intestine. They are produced in the liver and play a crucial role in metabolic regulation. Beyond their well-known function as detergents, bile acids also influence hepatic health by acting on liver cell receptors that regulate energy metabolism and homeostasis. Disruption in bile acid levels can lead to significant liver disease, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), pointing to the need for further understanding of bile acid dynamics.
Recent studies have highlighted the complex signaling pathways that regulate bile acid synthesis and its implications in liver diseases. Research indicates that an imbalance in bile acid composition can result in inflammation and fibrosis, which are precursors to liver cancer. By maintaining bile acid homeostasis, researchers believe it is possible to mitigate risks associated with liver disease and improve therapeutic outcomes.
Bile Imbalance Linked to Liver Cancer: YAP FXR Signaling Mechanisms
The intertwining pathways of YAP (Yes-associated protein) and FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) illustrate a significant mechanism behind bile acid imbalances leading to liver cancer. YAP is known to promote tumor growth, yet in the context of bile acid regulation, it acts intriguingly as a repressor of FXR activity. This dual function of YAP creates a scenario where bile acid overproduction occurs, resulting in liver inflammation and potential tumorigenesis, highlighting the necessity of investigating YAP FXR signaling specifically within liver cancer research.
Targeting this regulatory mechanism presents a novel avenue for liver cancer treatment interventions. By enhancing FXR activity or inhibiting YAP’s suppressive effects, researchers are exploring ways to restore bile acid balance, which could halt the progression of liver diseases, including HCC. These promising therapeutic strategies focus on leveraging the body’s own biochemical pathways to combat cancer and reduce the detrimental effects of bile acid imbalances.
Implications of Bile Acid Imbalance on Liver Disease Progression
The implications of bile acid imbalances extend beyond liver cancer diagnosis; they suggest a potential metabolic dysregulation prevalent in various liver diseases. In hepatocellular carcinoma, the accumulation of bile acids can exacerbate inflammation and fibrosis, creating an environment conducive to cancer development. Current liver disease research emphasizes the need for targeted therapies that stabilize bile acid levels to potentially reverse liver damage and improve patient outcomes.
Furthermore, understanding how bile acid imbalances contribute to liver disease progression can inform the development of tailored treatments. Researchers are focused on drug candidates that target bile acid signaling pathways, providing hope for patients suffering from advanced liver diseases such as HCC. As studies progress, the hope is to translate these findings into effective therapeutic strategies that address the underlying causes of bile-related liver damage.
Revolutionizing Liver Cancer Treatments Through Bile Research
Emerging research on bile acids has illuminated new pathways and targets for liver cancer treatment. The ability to manipulate the interplay between YAP and FXR provides researchers with exciting possibilities for creating innovative therapies. By controlling bile acid synthesis and excretion, it may be possible to reduce the risks of developing conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma, which remains a significant health concern worldwide.
The identification of molecular switches that influence bile composition opens doors not only for liver cancer treatments but also for broader applications in managing liver disease. As initiatives in liver disease research continue to evolve, the focus on bile acids underscores the critical role they play in metabolic health, reshaping the future of liver health treatment protocols.
Advancements in Liver Disease Research: The Role of Bile Acids
Recent advancements in liver disease research have revealed the pivotal role of bile acids in hepatic health and disease mechanisms. Studies focusing on pharmacological agents that enhance FXR functionality or inhibit YAP have shown promise in combating the overproduction of bile acids associated with liver diseases. This research is crucial for developing targeted therapies aimed at addressing metabolic dysfunctions that lead to serious liver conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
The commitment to understanding bile acid physiology represents a significant step forward in liver disease research. Upcoming studies aim to explore the entire spectrum of bile-related pathways, striving to establish a comprehensive understanding of how bile acids contribute to liver health and disease. This holistic approach could potentially transform the landscape of liver cancer treatment and prevention.
Liver Cancer Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of Bile Acid Modulation
Bile acid modulation has emerged as an exciting frontier in liver cancer treatment strategies. The recognition that bile acids play a regulatory role in liver metabolism highlights their therapeutic potential. By targeting pathways that control bile acid levels, researchers are developing innovative pharmacological solutions that could prevent or slow the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
This therapeutic approach not only aims to directly combat cancer cell proliferation but also seeks to restore hepatic balance and functionality. Current focus on FXR as a potential drug target opens new avenues for clinical applications, advancing the fight against liver cancer and enhancing the overall management of liver diseases. As research progresses, the integration of bile acid modulation into liver cancer treatment protocols could significantly improve patient outcomes.
The Connection Between Metabolism and Liver Cancer
A deeper understanding of the metabolic processes driven by bile acids is critical in the context of liver cancer. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism are often indicative of underlying liver pathology, including inflammation and malignancy. Investigating the relationship between bile acid profiles and liver disease progression can provide invaluable insights that inform diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Integrating metabolic profiling into liver cancer research enables a more comprehensive evaluation of how bile acids may influence tumor biology. This emerging field holds the promise of identifying novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets to improve detection, monitoring, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, leading to better prognoses for patients.
Future Directions in Bile Acid and Liver Disease Research
The future of liver disease research is poised to uncover further complexities related to bile acid imbalances and their consequences on liver health. With advancements in genomic and molecular techniques, researchers are increasingly able to dissect the intricate signaling pathways involved in bile acid metabolism. This comprehensive approach could yield new insights into disease mechanisms, paving the way for innovative treatment modalities.
Continued exploration of the relationship between bile acids and liver cancer will likely lead to breakthroughs in prevention and treatment strategies. By focusing on the regulatory mechanisms that influence bile acid homeostasis, researchers aim to develop targeted interventions that not only treat liver cancer but also promote overall liver health, potentially revolutionizing patient care in hepatology.
Interdisciplinary Approaches to Bile and Liver Cancer Research
The complexity of bile acid metabolism and its implications for liver cancer necessitate interdisciplinary approaches to research. Collaboration among hepatologists, molecular biologists, and pharmacologists is crucial to unlocking the potential of bile acids in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases. This teamwork fosters the sharing of knowledge and expertise that can accelerate the discovery of effective therapies.
Through collaborative efforts, innovative strategies to target dysregulated bile acid signaling pathways can be developed. For instance, incorporating genetic insights and cutting-edge technology into research may yield a more nuanced understanding of how bile acids influence liver pathology and disease progression. This collaborative approach signifies a promising future in the fight against liver cancer, enhancing the efficacy of treatment interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the link between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is a significant factor in liver diseases, including liver cancer. Specifically, an imbalance in bile acids may lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are precursors to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. Disruption in bile acid metabolism can trigger a cascade of biological processes that culminate in cancer development.
How do bile acids influence liver cancer treatment options?
Bile acids play a crucial role in liver health and disease. Research indicates that regulating bile acid metabolism might provide new liver cancer treatment opportunities. Therapies that enhance the function of bile acid sensors like FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) or promote bile acid excretion could potentially reduce liver damage and slow cancer progression, offering a targeted approach in liver cancer treatment.
What role does YAP FXR signaling play in bile imbalance and liver cancer?
YAP FXR signaling is vital in maintaining bile acid homeostasis. In liver cancer, the YAP protein can inhibit FXR function, leading to bile acid overproduction and subsequent liver inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma. Targeting this signaling pathway may present new therapeutic avenues for managing bile imbalance and liver cancer.
Can liver disease research lead to advancements in liver cancer treatment?
Yes, liver disease research is crucial for advancing liver cancer treatment. Studies that explore the relationship between bile acids, liver signaling pathways, and cancer progression provide insights that can inform the development of targeted treatments, such as drugs that activate FXR to restore bile acid balance and mitigate liver disease.
What are the implications of high bile acid levels for liver health?
High bile acid levels can lead to liver damage, inflammation, and ultimately increase the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. The accumulation of bile acids is associated with fibrosis and disruption of liver function, indicating that monitoring and managing bile acid levels may be critical in preventing liver disease and cancer.
How can inhibiting YAP’s repressive function aid in liver cancer prevention?
Inhibiting YAP’s repressive function may help restore the regulatory balance of bile acid metabolism. This can be achieved by enhancing the action of FXR or increasing bile acid excretion, which could reduce liver injury and the associated risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, thereby providing a novel approach for liver cancer prevention.
What current research is addressing bile acids and liver cancer?
Current research, such as that conducted by Yingzi Yang and her team, focuses on understanding the mechanisms by which bile acids affect liver health and their role in liver cancer development. Studies investigating the interaction between YAP FXR signaling and bile acid metabolism are paving the way for innovative treatment strategies aimed at mitigating liver cancer risk.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Bile imbalance is linked to liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver’s bile production is crucial for fat digestion and metabolic regulation. |
| A study published in Nature Communications identified a key molecular switch affecting bile acid regulation, leading to insights into liver cancer treatments. |
| YAP protein promotes tumor formation while inhibiting the critical bile acid sensor, FXR, leading to liver damage and cancer. |
| Therapeutic strategies may involve enhancing FXR function or increasing bile acid excretion to combat liver damage. |
| The research emphasizes the importance of cell signaling in regulating bile acids, potentially influencing broader metabolic control. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer has emerged as a significant health concern, with recent studies highlighting the role of bile acid regulation in the development of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Research indicates that disruptions in bile production and metabolism can lead to liver injury and cancer progression. Understanding the molecular mechanisms involved in bile imbalance can pave the way for innovative treatments targeting liver cancer, particularly through the modulation of key proteins like YAP and FXR. This continued research is crucial for developing new therapeutic strategies that could significantly impact patient outcomes.
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | |||||