Alzheimer’s Early Detection: New Home Test for Cognitive Risks
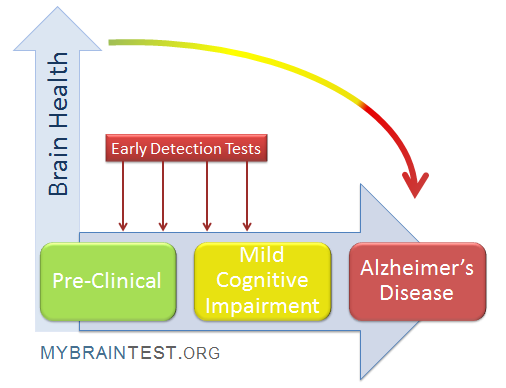
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial in the fight against this pervasive neurodegenerative disease, enabling timely interventions that can significantly improve quality of life. Recent advancements have highlighted innovative methods, such as an olfactory test that assesses cognitive impairment detection through a simple at-home sniffing exercise. This groundbreaking study from Mass General Brigham showcases how participants can identify odors, shedding light on early memory loss symptoms linked to Alzheimer’s. Senior researcher Mark Albers emphasized that recognizing these initial signs could allow for proactive strategies to manage Alzheimer’s disease years before cognitive decline manifests. By focusing on such tests, we can pave the way for improved Alzheimer’s testing and a deeper understanding of how to combat memory loss effectively.
The early identification of Alzheimer’s disease indicators is becoming increasingly critical as researchers pursue methods to anticipate the onset of cognitive challenges. Utilizing various assessment tools, including scent-based evaluations, scientists aim to detect subtle changes in cognitive function that may predict future impairment. Conditions associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as memory loss and olfactory dysfunction, have become focal points in this area of exploration. By exploring these alternative approaches, we enhance our understanding of cognitive decline and enable timely intervention for those at risk. This proactive framework aims to empower individuals and caregivers alike, transforming the landscape of Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial for effective intervention and treatment. Research indicates that identifying cognitive impairment before significant memory loss occurs enhances the possibility of managing the disease’s progression. This proactive approach focuses on recognizing the initial signs of cognitive decline, allowing healthcare providers to tailor suitable strategies for patients, from lifestyle modifications to pharmacological treatments.
The development of innovative tools, such as the olfactory test, marks a significant leap in Alzheimer’s early detection strategies. Individuals may not realize they are displaying symptoms of memory loss or other cognitive impairments, which is why early testing becomes essential. By utilizing simple, non-invasive methodologies, such as odor identification tests, patients can partake in at-home assessments that could reveal early signs of neurodegenerative diseases.
The Role of Olfactory Testing in Alzheimer’s Screening
Recent studies have revealed the connection between olfactory dysfunction and early signs of Alzheimer’s disease. The olfactory test developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham positions itself as a promising screening tool to detect cognitive impairment. Participants are asked to identify various odors, with results indicating that individuals with cognitive impairments score significantly lower compared to their cognitively normal counterparts.
This olfactory testing approach not only provides a cost-effective solution for Alzheimer’s screening but also empowers patients to perform the tests in comfortable settings, such as their homes. Continued research in this area can enhance the understanding of how sensory deficits, particularly in smell, correlate with neurodegenerative progression, thereby facilitating earlier and more effective interventions for at-risk individuals.
Symptoms of Cognitive Impairment: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Memory loss symptoms often manifest subtly and can be easily overlooked in daily life. Individuals might forget conversations or repeat questions, which may be dismissed as normal aging. However, when these memory lapses are frequent and begin to interfere with everyday activities, it may indicate underlying cognitive impairment or potential neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Prompt recognition of these symptoms is critical, as it opens avenues for early testing and intervention. Engaging with healthcare professionals upon noticing such changes can lead to necessary evaluations, including cognitive tests or olfactory assessments, to ascertain the presence and extent of impairment, ensuring timely management of an individual’s health.
Neurodegenerative Disease Signs and Their Impact
Understanding the signs of neurodegenerative diseases is vital for caregivers and loved ones. These diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, often present with various symptoms, including cognitive decline and motor issues. Being aware of these signs can significantly impact early diagnosis and treatment strategies, improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
Common signs include gradually worsening memory loss, difficulty in problem-solving, and changes in mood or personality. Families and caregivers should monitor these changes closely, as awareness can prompt timely medical evaluations, paving the way for early detection methods, including olfactory testing.
The Importance of Cognitive Impairment Detection
Detecting cognitive impairment early is essential in addressing the challenges associated with Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative conditions. Traditional methods of diagnosis often come late in the progression of the disease, limiting the efficacy of treatment options. With ongoing research, strategies like olfactory tests provide an innovative approach to identifying cognitive decline before the full onset of debilitating symptoms.
Moreover, early cognitive impairment detection can lead to more personalized care plans and interventions. Educating the public about the value of recognizing and reporting early signs can help destigmatize the conversation around memory loss, promoting proactive health measures and early engagement with healthcare professionals.
Innovations in Alzheimer’s Testing: The Aromha Brain Health Test
Innovations such as the Aromha Brain Health Test represent a significant advancement in Alzheimer’s research. This at-home olfactory test allows individuals to evaluate their memory function by identifying and distinguishing various scents. This method provides a viable alternative for those who may have difficulty accessing traditional testing facilities.
With its non-invasive nature and cost-effectiveness, the Aromha Brain Health Test can facilitate greater participation in cognitive assessments. As more individuals engage in these early detection tests, we may uncover more insights into the progression of neurodegenerative conditions and refine our understanding of cognitive health.
Cognitive Health: Addressing community needs through research
Research into cognitive health is vital not only for affected individuals but also for their communities. Understanding how cognitive decline affects not just personal health, but social structures and economic systems, underscores the importance of prioritizing research funding and public awareness in Alzheimer’s and cognitive impairment studies.
Emerging data highlights the critical need for comprehensive strategies that include community education, awareness programs, and accessible testing methodologies. Collaborating across sectors can create a supportive framework for early detection and intervention, enhancing overall community resilience against neurodegenerative diseases.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research: A Collaborative Endeavor
The future of Alzheimer’s research points toward a collaborative approach, interfacing various disciplines to tackle cognitive health comprehensively. Through networks of researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers, the goal is to enhance understanding, improve detection methodologies, and create effective treatment protocols.
Ongoing studies exploring innovative testing options, such as olfactory assessment, are pivotal in this collaborative sphere. By fostering dialogue and partnership, stakeholders can work towards establishing effective frameworks that support individuals at risk, ultimately advancing the fight against Alzheimer’s disease.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments for Cognitive Health
While early detection plays a crucial role in managing Alzheimer’s, preventive measures must not be neglected. Engaging in a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and mental exercises, can mitigate risk factors associated with cognitive decline. These proactive steps contribute significantly to long-term cognitive health.
Additionally, community programs aimed at educating individuals on the importance of cognitive health can further enhance preventative strategies. By spreading awareness about lifestyle changes, such as improved nutrition and brain-stimulating activities, communities can empower individuals to take charge of their cognitive well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is involved in an Alzheimer’s early detection test?
An Alzheimer’s early detection test may include cognitive assessments, such as olfactory tests, where individuals identify and remember different odors. Researchers from Mass General Brigham have developed a home test that focuses on odor discrimination, which has shown that older adults with cognitive impairment score lower compared to cognitively normal individuals.
How does olfactory testing help in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease?
Olfactory testing aids in Alzheimer’s early detection by identifying subtle changes in the sense of smell, which can be an early warning sign of neurodegenerative diseases. This noninvasive method can help identify individuals at risk before memory loss symptoms begin, offering a pathway for intervention and research.
What are common memory loss symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s disease?
Common memory loss symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s disease include difficulty remembering recent events, trouble planning or solving problems, and confusion about time or place. These cognitive impairment signs often emerge as the disease progresses, but early detection methods aim to spot these issues before significant symptoms appear.
Can Alzheimer’s early detection tests be done at home?
Yes, Alzheimer’s early detection tests, like the olfactory test developed by researchers, can be performed at home. These tests involve simple tasks, like identifying odors, and have been designed to be effective and easily accessible for individuals concerned about cognitive impairment.
What role does cognitive impairment detection play in Alzheimer’s research?
Cognitive impairment detection is crucial in Alzheimer’s research as it helps identify individuals at risk. Early detection allows for timely interventions and the chance to study potential treatments before significant memory loss symptoms develop, enhancing our understanding of the neurodegenerative disease.
Are there specific tests for detecting cognitive impairment related to neurodegenerative diseases?
Yes, there are specific tests for detecting cognitive impairment related to neurodegenerative diseases, such as the olfactory test recently developed. This type of test evaluates an individual’s ability to identify and remember smells, serving as an early indicator of conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Background | Study conducted by researchers at Harvard-affiliated Mass General Brigham. |
| Olfactory Tests | At-home tests involving sniffing odor labels to assess cognitive function. |
| Participant Types | Included older adults with cognitive impairment and self-reported memory concerns. |
| Study Findings | Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower than cognitively normal adults. |
| Olfactory Dysfunction | Could serve as an early warning sign for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Clinical Implications | A cost-effective, noninvasive test that can potentially predict cognitive decline. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is becoming increasingly important in the fight against cognitive decline. A recent study reveals that olfactory tests can identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s disease long before symptoms appear. This innovative approach not only highlights the potential for early intervention but also provides a simple, at-home testing method that can support future research and treatment advancements. By recognizing the subtle changes in our sense of smell, we may pave the way for more effective strategies to combat Alzheimer’s and enhance brain health.
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |